Blind Audio Source Separation - Musical
We deal with the case where the sources are linearly mixed and the
mixtures are underdetermined. Hence, A has more columns than rows.
Sparsity of the sources is vital for good separation. Bayesian methods
such as the Gibbs Sampler (a standard MCMC simulation method) are used
to estimate the sources and the mixing matrix in the presence of noise.
I.I.D. Gaussian noise was added to the observations, which resulted in
an SNR of about 16 dB. The mixing matrix used is given by A = [0.4000
0.8315 0.5657; -0.6928 -0.3444 0.5657].
3) Muscial Signals
These are the 3 musical signals.
Musical Signal 1
Arab Strap Guitar
Musical Signal 2
Piano
Musical Signal 3
Guitar
These are the 2 mixtures.
Mixture 1
Mixture 2
Sparsity Indices for various transform types.
Click on thumbnails for larger (and clearer) versions.
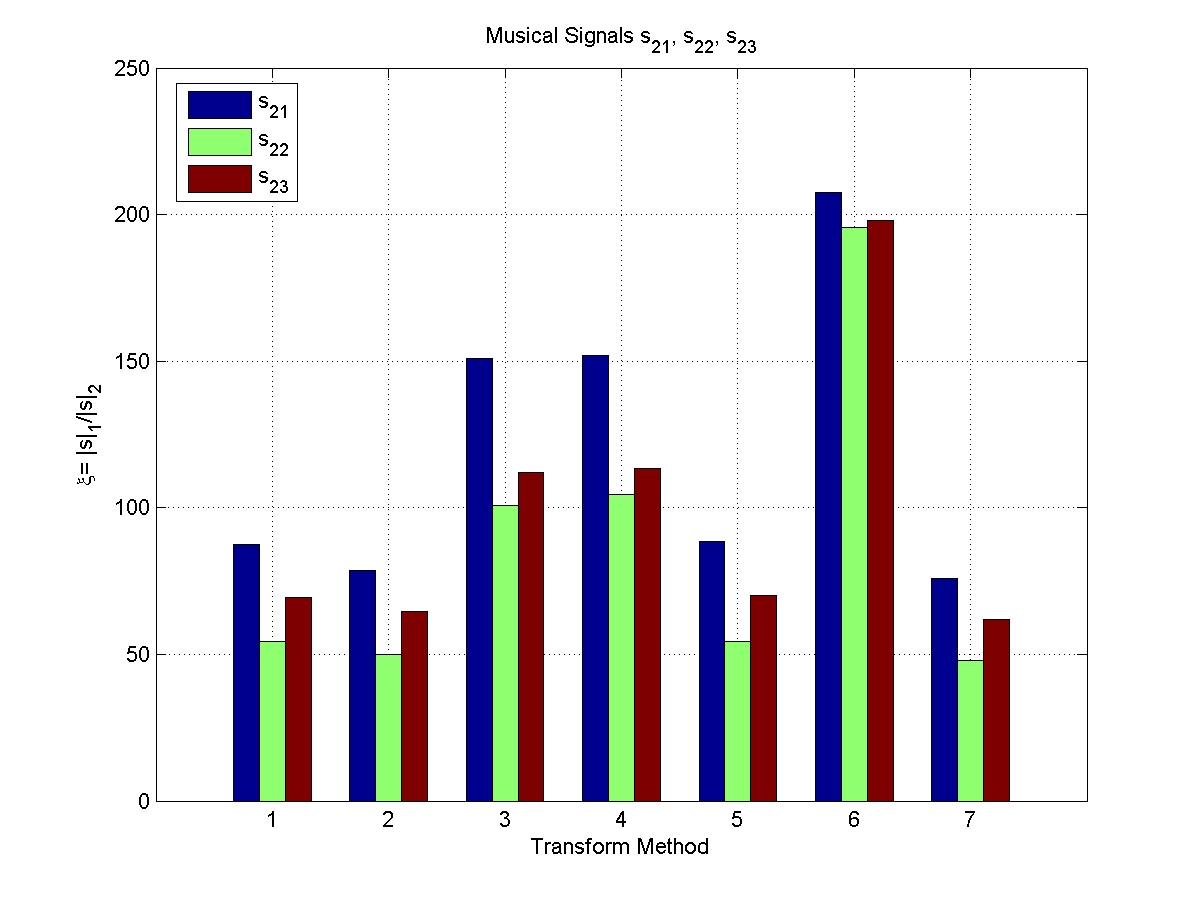
Transform Types
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
| DCT |
MDCT |
WT (Vai) |
WT (Sym8) |
WPBB |
No Transform |
Results at a glance.
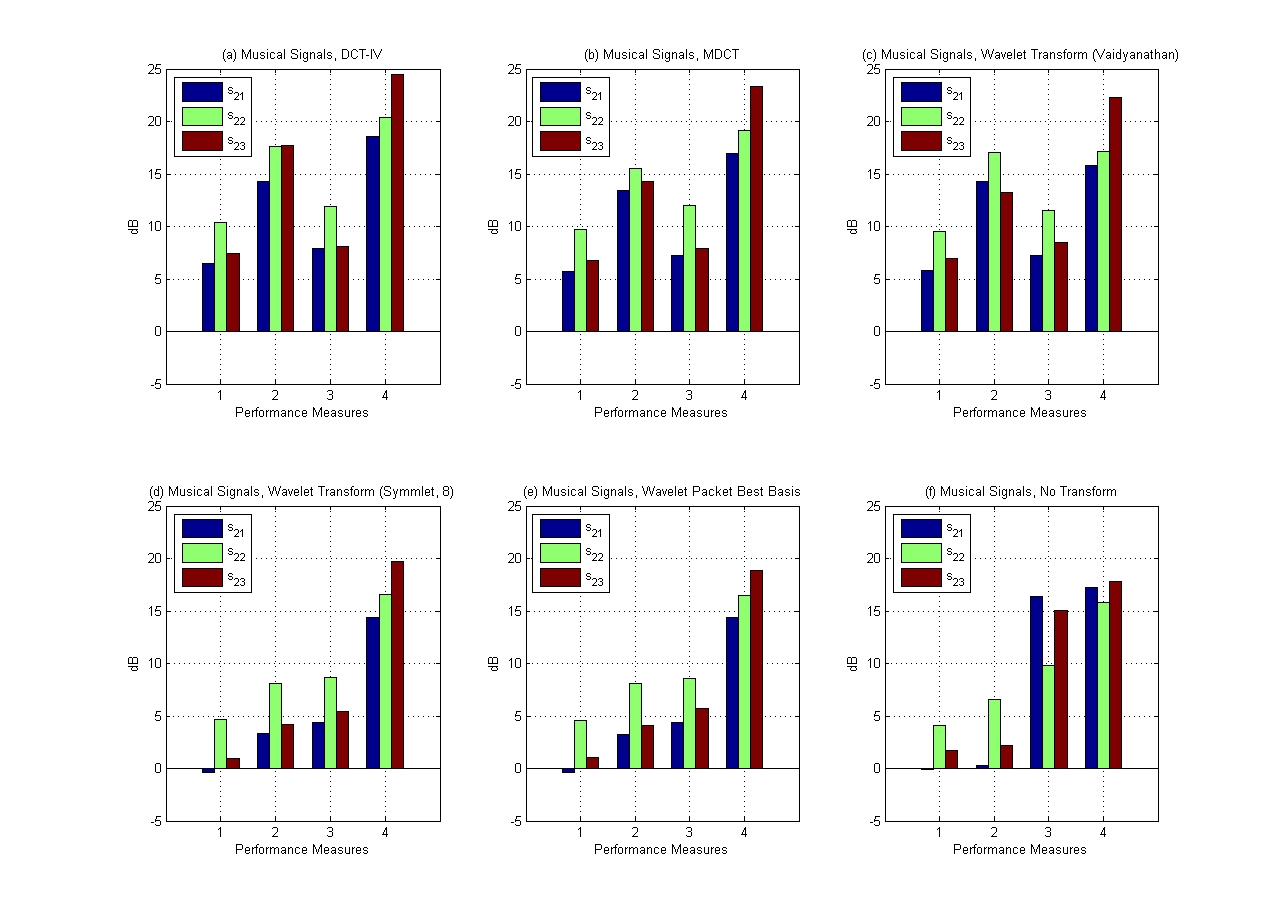
Performance Measures
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| SDR |
SIR |
SAR |
SNR |
3.1) Discrete Cosine Transform
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
3.2) Modified Discrete Cosine Transform
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
The MDCT is the obvious transform to achieve sparsity for
"conventional" sources like pure music.
3.3) Wavelet Transform: Vaidyanathan
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
The reconstructed sources are unnatural when one uses wavelets.
This is unsurprising given that wavelets model the transients well but
musical signals are composed mainly by tonals.
3.4) Wavelet Transform: Symmlet 8
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
The reconstructed sources are unnatural when one uses wavelets.
This is unsurprising given that wavelets model the transients well but
musical signals are composed mainly by tonals.
3.5) Wavelet Packet Best Basis
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
An adaptive algorithm will provide reasonable separation.
The performance indices are identical to the DCT but slightly worse
than the MDCT.
The difference in sound quality is similar to the MDCT and DCT but
noise suppression is marginally worse.
3.6) No Transform
Reconstructed Musical Signal 1
Reconstructed Musical Signal 2
Reconstructed Musical Signal 3
No separation without an appropriate transform.
Musical sources are not sparse in physical space.
Back
Next
Home
Server at www.eng.cam.ac.uk